E-textiles and Wearables II
Assignment for this week was to create an interactive object.
For this project, I used an Arduino and an Accelerometer-Gyroscope GY-521 MPU6050.
The MPU6050 contains both a 3-Axis Gyroscope and a 3-Axis accelerometer allowing measurements of both independently, but all based around the same axes, thus eliminating the problems of cross-axis errors when using separate devices.

Specifications
Accelerometer ranges /-2, /-4, /-8, /-16g
Gyroscope ranges: /-250, 500,1000, 2000 degree/s
Voltage range:3.3V-5V ( the module include a low drop-out voltage regulator).
This module contains everything required to interface to the Arduino and other controllers via 12C and give motion sensing information for 3 axes -X, Y, Z.
I connected the module- to-Arduino this way:
SDA-A4
SCL-A5
VCC-5v
GND-GND
INT-pin2
The following libraries were necessary to download and be put on the Arduinos libraries folder in order for me to understand better the module and read his values.
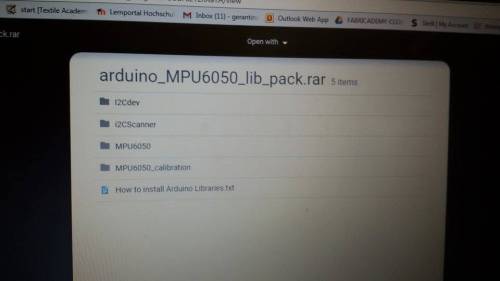
Then I went to my arduino and run the sketch I2C_scanner and read the values on the serial monitor.
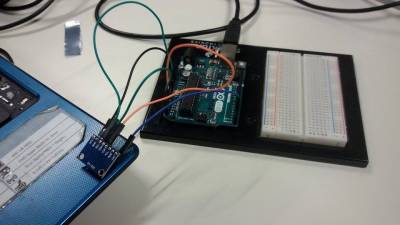
By moving the module I was observing his values and wrote down which values are showing a fall in all 4 directions.
Then I used the following code provided from githube and changed the values in this code according to my gyroscope values.
#include <Wire.h> //library used for I2C communication long accelX, accelY, accelZ; //data read from MPU itself float gForceX, gForceY, gForceZ; long gyroX, gyroY, gyroZ; float rotX, rotY, rotZ; void setup() { Serial.begin(115200); Wire.begin(); setupMPU(); } void loop() { recordAccelRegisters(); recordGyroRegisters(); printData(); delay(100); } void setupMPU(){ //establish comunication with MPU, setup registergs used to read data Wire.beginTransmission(0b1101000); //This is the I2C address of the MPU (b1101000/b1101001 for AC0 low/high datasheet sec. 9.2) Wire.write(0x6B); //Accessing the register 6B - Power Management (Sec. 4.28) Wire.write(0b00000000); //Setting SLEEP register to 0. (Required; see Note on p. 9) Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.beginTransmission(0b1101000); //I2C address of the MPU Wire.write(0x1B); //Accessing the register 1B - Gyroscope Configuration (Sec. 4.4) Wire.write(0x00000000); //Setting the gyro to full scale /- 250deg./s Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.beginTransmission(0b1101000); //I2C address of the MPU Wire.write(0x1C); //Accessing the register 1C - Acccelerometer Configuration (Sec. 4.5) Wire.write(0b00000000); //Setting the accel to /- 2g Wire.endTransmission(); } void recordAccelRegisters() { Wire.beginTransmission(0b1101000); //I2C address of the MPU Wire.write(0x3B); //Starting register for Accel Readings Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(0b1101000,6); //Request Accel Registers (3B - 40) while(Wire.available() <6); accelX = Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); //Store first two bytes into accelX accelY = Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); //Store middle two bytes into accelY accelZ = Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); //Store last two bytes into accelZ processAccelData(); } void processAccelData(){ gForceX = accelX / 16384.0; gForceY = accelY / 16384.0; gForceZ = accelZ / 16384.0; } void recordGyroRegisters() { Wire.beginTransmission(0b1101000); //I2C address of the MPU Wire.write(0x43); //Starting register for Gyro Readings Wire.endTransmission(); Wire.requestFrom(0b1101000,6); //Request Gyro Registers (43 - 48) while(Wire.available() <6); gyroX = Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); //Store first two bytes into accelX gyroY = Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); //Store middle two bytes into accelY gyroZ = Wire.read()<<8|Wire.read(); //Store last two bytes into accelZ processGyroData(); } void processGyroData() { rotX = gyroX / 131.0; rotY = gyroY / 131.0; rotZ = gyroZ / 131.0; } void printData() { Serial.print("Gyro (deg)"); Serial.print(" X="); Serial.print(rotX); Serial.print(" Y="); Serial.print(rotY); Serial.print(" Z="); Serial.print(rotZ); Serial.print(" Accel (g)"); Serial.print(" X="); Serial.print(gForceX); Serial.print(" Y="); Serial.print(gForceY); Serial.print(" Z="); Serial.println(gForceZ); }
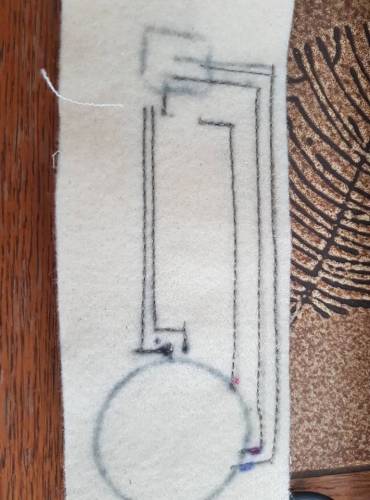
I wanted to integrate the system in a belt using the conductive thread as wires and a lilypad. I first tried to a small version to see if I could make the idea work.
 I
I
I used the sawing machine to saw but unfortunately, the connection was very weak. I used a voltmeter to check the connection and from one side of the connection to the other the resistance was or very high or didn't show any connection at all.
For a time I was still thinking or how to ingrate the system but wasn't successful so when me and Melissa where doing our final project I first tried this assigment on the armband and was working.